Sharp’s History of Solar Business
A track record of over 60 years
In 1959, Sharp became the first company in the world to embark on research and development into solar cell devices. Sharp's solar products are at work in many areas: on homes, in extreme environments such as lighthouses and artificial satellites, and in megawatt-scale solar power plants around the world. Sharp's track record of over half a century has earned it a solid reputation in the world of solar.

Founder Tokuji Hayakawa
- 1959
- Started development of solar cells

- 1963
- Succeeded in the mass production of single-crystal solar cells

- 1966
- Lighthouse on Ogami Island in Nagasaki equipped with Sharp solar modules (225W, the world's largest at the time)

- 1976
- Japan's first operational satellite for space, called “Ume”, equipped with Sharp solar cells

- 1983
- 40 units of 36-cell solar modules for illuminating the Big Buddha at Tsubosaka-dera Temple (Nara)

- 2010
- Sharp's commercialization and industrialization of solar cells recognized as an IEEE Milestone
Other IEEE Milestones in Japan
- Shinkansen (1964) → Recognized in 1999
- Electronic calculator (Sharp, 1964–1973) → Recognized in 2005
- Railroad ticket examining system (1965–1971) → Recognized in 2007

- 2012
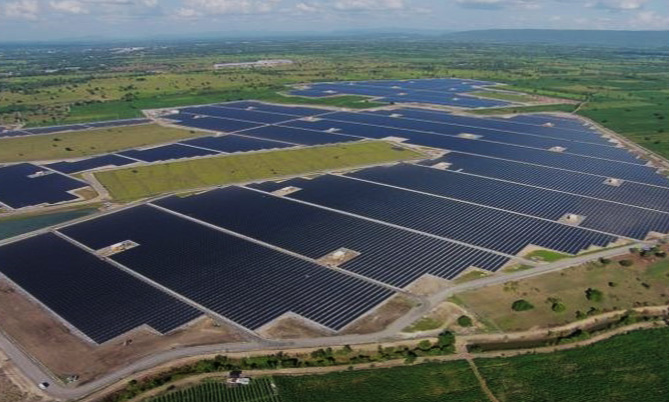
- Utility-scale solar power plant built in Thailand
- Proved resistance to PID (potential induced degradation) at Europe's largest research institute

- 2013
- Started IPP (independent power producer) business in Japan using megawatt-scale solar power
Achieved 37.9% conversion efficiency, the world's highest, for triple-junction compound solar cells

- 2014
- Sharp solar cells installed in the Daichi 2 Advanced Land Observation Satellite of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)

- 2015
- Released BLACKSOLAR panels, which use monocrystalline solar cells to achieve 19.1% module conversion efficiency


- 2016
- Achieved 31.17% conversion efficiency, the world's highest in solar modules, using triple-junction compound solar cells
Released LN-CA2A solar-powered charging stand for smartphones


- 2017
- Received order for rooftop solar power system installation from a supermarket chain in Thailand
Completed first megawatt-scale solar power plant in Mongolia


- 2018
- Achieved 25.09% conversion efficiency, the world's highest, for 6-inch monocrystalline solar cells
Began operation at Vietnam's first megawatt-scale solar power plant
Sharp Energy Solutions Corporation (SESJ) took over Sharp Corporation's energy business
Strict quality testing and long-term durability
Sharp solar panels—vital to generating power—undergo a range of proprietary Sharp in-house tests that are much stricter than the equivalent standards under IEC*1, JIS*2, and other institutions.
Such testing enables Sharp panels to last longer, a crucial factor in the power generation business.
- *1 Standards stipulated by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), an international organization that prepares and publishes international standards for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. The IEC standards here refer to IEC 61215 (ed. 2) for performance and reliability and IEC 61730-2 (ed. 1) for safety.
- *2 Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS). JIS standards are the Japanese national standards established for the standardization and measurement methods of industrial products in Japan.
Quality testing based on strict proprietary Sharp standards
High temperature and humidity test, humidity freeze test, PID (potential induced degradation) test

Mechanical load test

We put our over 60 years of expertise in solar business into product evaluation to ensure we can provide high-quality products that give long-term, stable operation even under extreme conditions, be it wind, rain, high temperature and humidity, accumulated snow, frost, or salt air.
Sharp Solar—at work around the world
More than 1 million customers worldwide
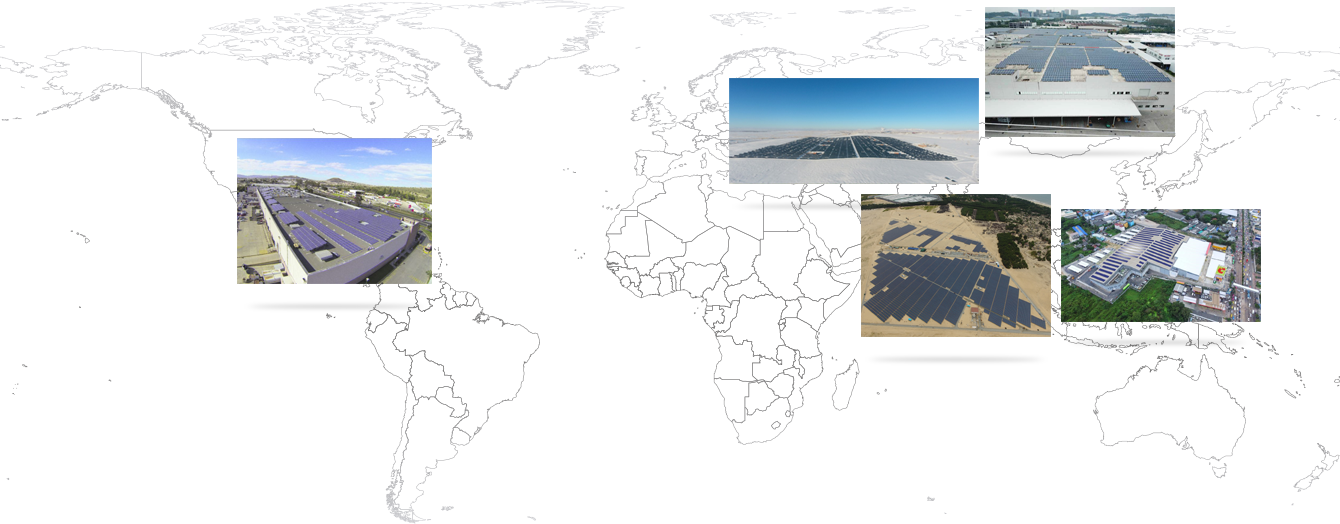
Sharp is the solar pioneer, the world's first company to launch a photovoltaic power business.
Sharp meets customer needs by offering fast and flexible solar solutions.


 Worldwide
Worldwide

